Wagan Tech’s 40 Amp DC to DC Charger
It takes some type of fuel or energy to power things, this includes humans as without food (and other necessities) our systems will shut down. In the case of our beloved Cummins-powered trucks, that energy comes from burning #2 diesel fuel. The primary output of the internal combustion is propulsion of the drivetrain; however, supporting systems give and take from the consumption, including the cooling and electrical charging systems.
Some readers know that the simple diesels from decades past would essentially run forever once started as long as the fuel flowed. They could be hard to cold-start, but they were also difficult to stop. This is because all diesels are ignited using compression ignition (CI), not a spark-ignition (SI) system like a traditional gasoline motor. Diesels are less complex without spark plugs, a coil, distributor cap and rotor, or wires, and while still fundamentally true there are modern complexities, chiefly the electronic fuel-injection.
Mandatory Electricity
Our newer, specialized, computer-controlled diesels need their modules to remain awake for everything to work properly (just like gas-powered trucks). Additionally, late-model vehicles are chock-full of countless electronic gizmos, from computer screens, cameras, seat and steering-wheel heaters, and the list goes on. The constant generation of electrical current from an alternator is no longer optional to keep the oil burning, but absolutely essential, even for daylight driving, because battery storage capacity is finite and amps consumed must be replaced.
High-output alternators easily handle the load of the Cummins cold-start grid heater, or the glow plugs in other automotive diesels, plus the increasingly popular factory-installed inverters that convert the DC current to 120-volt AC to power tools or other plug-in devices. But what about additional intermittent or constant 12-volt DC electrical loads?
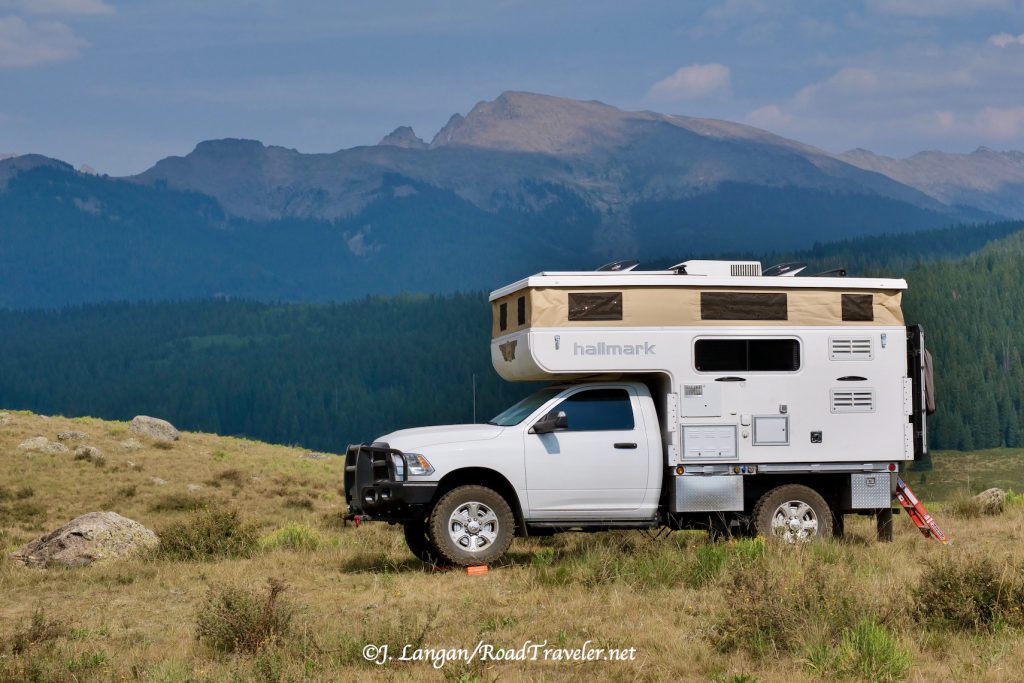

RV Amps
The TDR readership has always included a large percentage of RVers, and because we love our pickups so much, that means mostly travel trailers, big fifth-wheels, or truck campers instead of motorhomes. Solar panels atop an RV to charge coach batteries have been common for several years, as are backup generators to energize power-hungry AC appliances like microwaves and air-conditioners when shore power isn’t available. The solar panels require sunshine, and internal-combustion generators require fuel, so additional free amperage sources are welcomed.
When an RV is connected to a truck via the 7-way trailer-towing outlet, typically a small amount of juice is delivered to the RV to help charge the coach batteries, often somewhere around 10-amps. The limitation is not alternator capability, but the size of the factory wiring. This small amount of amperage can help keep charged batteries topped if there are minimal loads; however running high-draw devices can lead to deficits.
Modern Electric-Only Refrigerators
Like modern trucks full of gadgetry, newer RVs can have unprecedented amperage draws as well. The easiest example comes from the overlanding culture where electric refrigerators pioneered the replacement of traditional RV refrigerators, which principally ran on propane or 120 volts AC when plugged-in. Some older RV refers were theoretically capable of running on 12 V-volts, but they were terribly inefficient and would drain batteries fast.
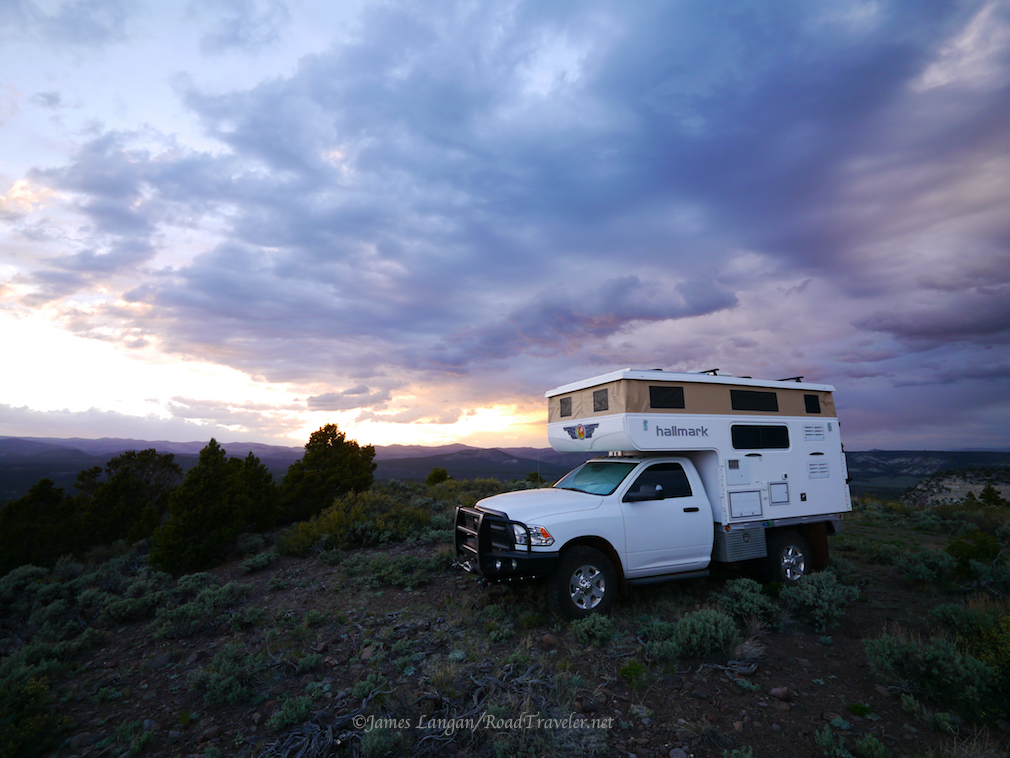
Instead of using the gas absorption method of cooling with propane, modern 12-volt refrigerators have a compressor, similar to the refrigerators in our homes. These can be built-in units, as in my Hallmark Camper, or a portable chest type refrigerator/freezer. These electric refrigerators are generally more efficient and effective, particularly in hot weather, and do not have to be leveled like a traditional RV refrigerator.
The benefits are being appreciated by more folks all the time, and in the off-grid and overland camping crowd electric fridge/freezers are seen as more rugged and vastly superior. Even the traditional RV market has noticed. My cousin recently purchased a new fifth-wheel trailer to live in (temporarily) after selling his house, and the refrigerator is 12-volt and 120-volt only, it doesn’t run on propane. There is at least one drawback and that is amperage consumption.
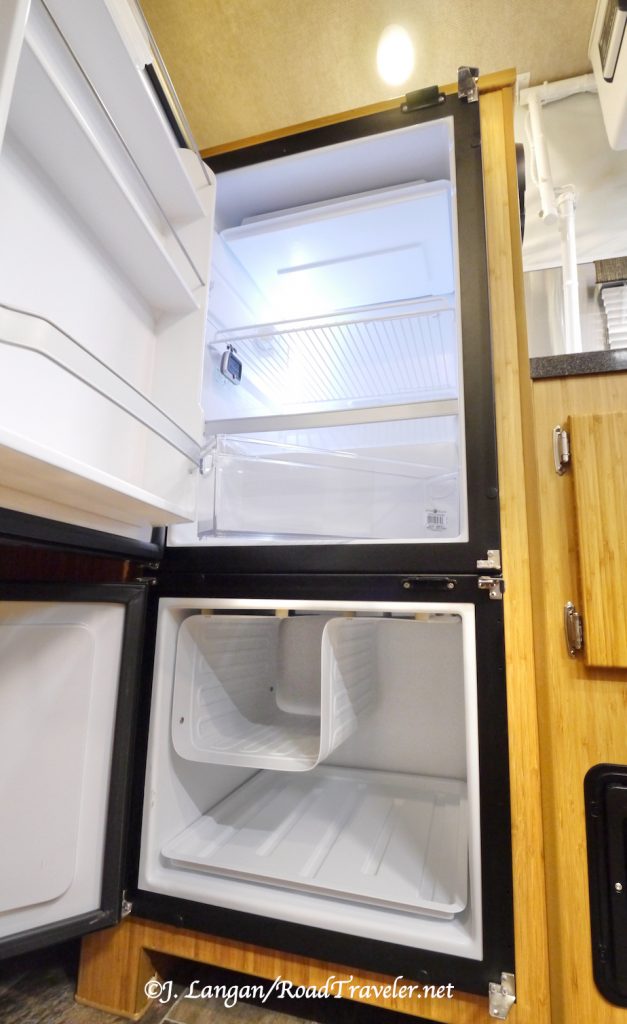

Additional Electrical Loads
The large-for-a-truck-camper NovaKool refrigerator with a separate freezer door in my Hallmark Flatbed consumes up to 5-amps when running, and it runs a lot during the summer months. Five amps per hour adds up quickly, pulling a chunk of the total 200 amp-hour capacity we have from two, 100-amp Battle Born lithium batteries.
My Hallmark is well sealed, but no RV is or can be impervious to dust, they need to breath like a house. With this in mind, and because I spend much time traveling off-pavement and nearly always camp in the dirt, I run one of my roof vent fans while driving to pressurize the living space. This works impressively well to minimize dust intrusion. There is one more big electrical draw inside my camper every 24 hours.
Although I do not fit the physical stereotype (I’m tall and slim), I use a CPAP machine to help me breathe and sleep every night. This is another substantial electrical draw, a minimum of 4-amps, even with a dedicated 12-volt cord to avoiding the inefficiencies of an inverter. Multi-day road trips with lots of driving still result in a battery charging deficit because the factory RV 7-way provides minimal amperage. The 340-Watts of solar panels help, but they are insufficient to keep the camper batteries charged due to my consumption. A small 700-Watt 2-stroke generator travels in one of the under-bed toolboxes as an emergency back up. I prefer not to use it, and it produces a mere seven amps. So how can one easily generate more electricity?
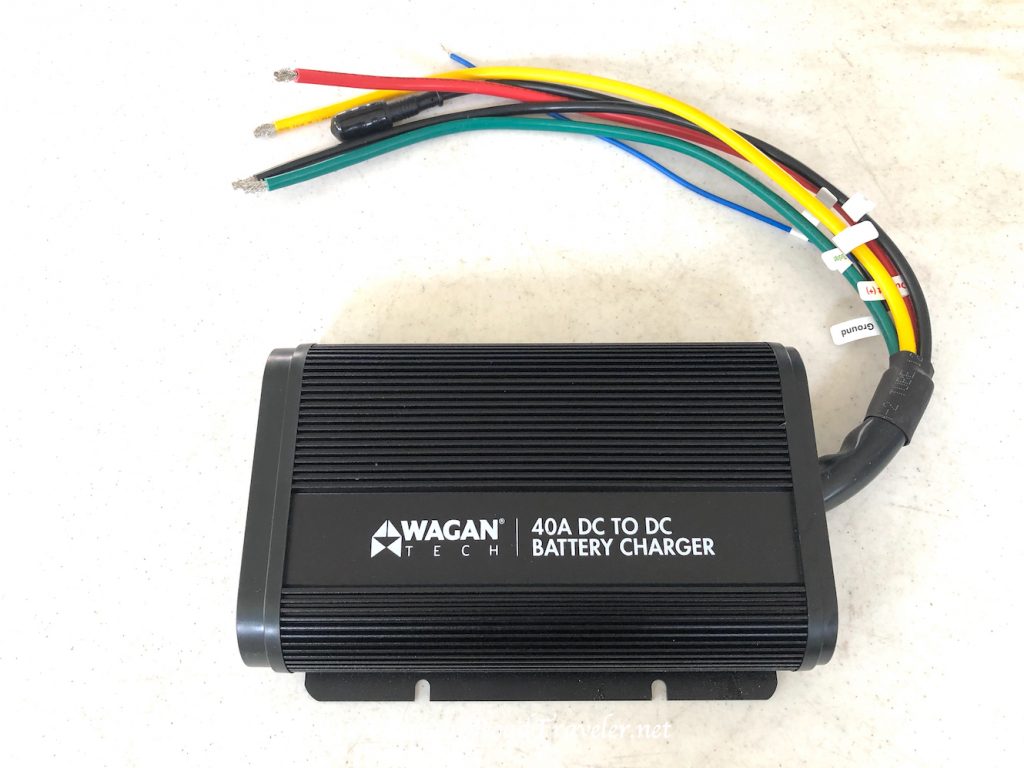

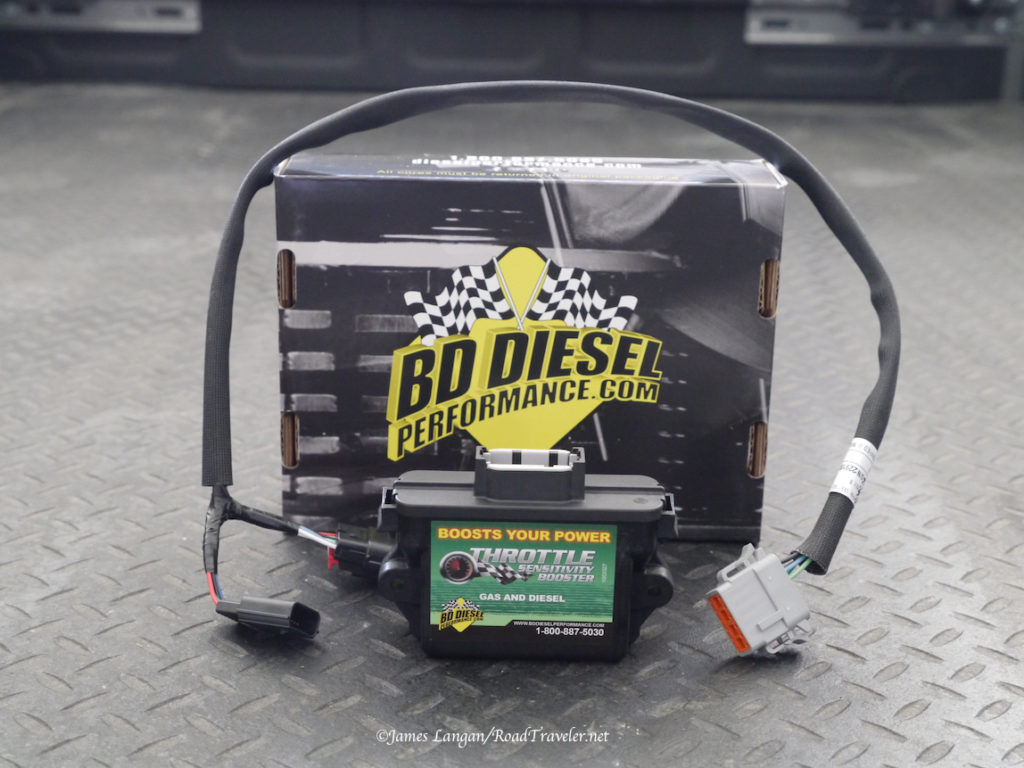
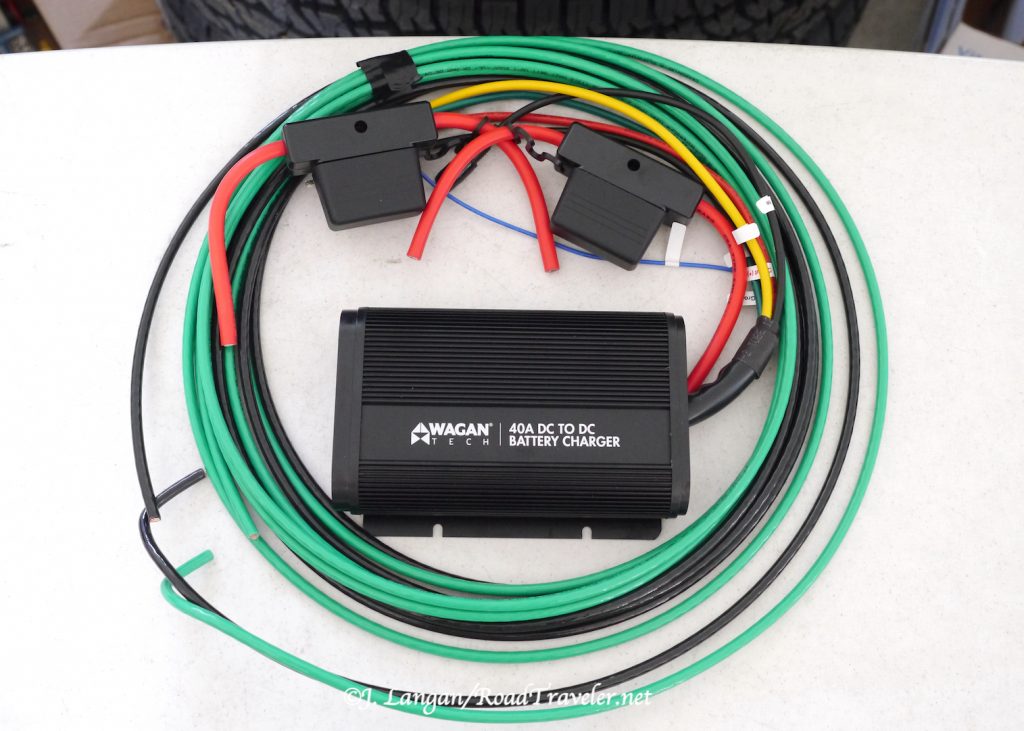
Wagan Tech 40 Amp DC To DC Battery Charger
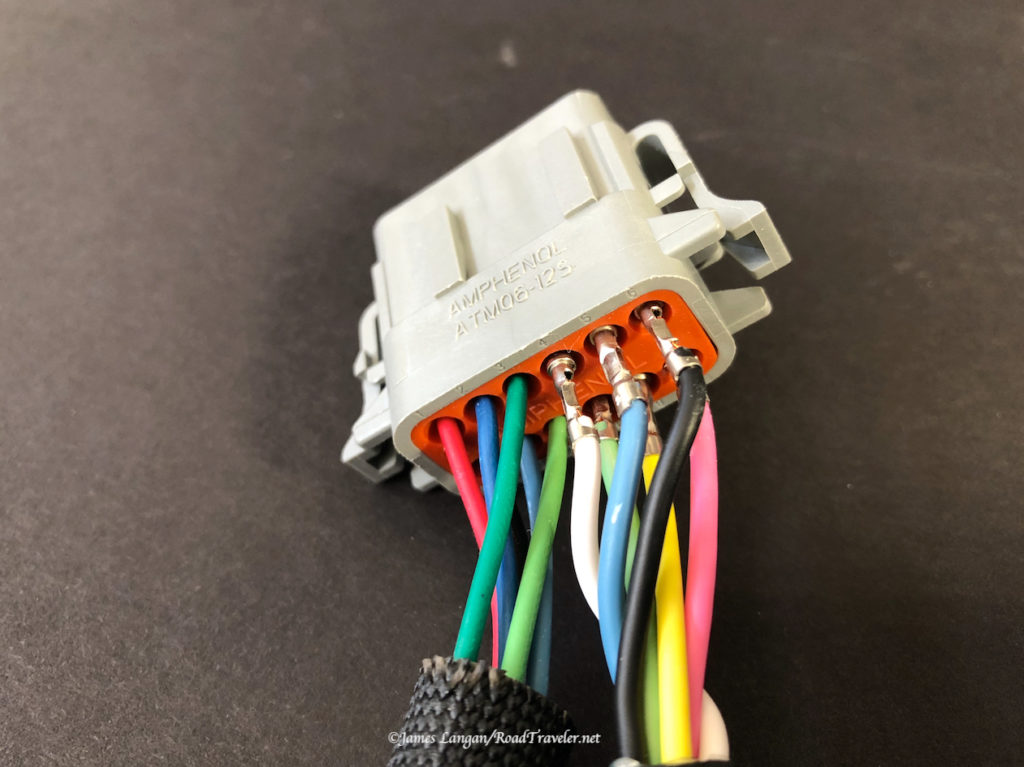
DC to DC battery chargers have been around a few years. They are popular in places like Australia, where the off-pavement backcountry travel market has historically been more robust and innovative. These devices are exactly what they sound like, taking DC amperage from the battery/alternator charging system under the hood and feeding it directly to auxiliary (RV) batteries through large wires. Sounds simple, and it is. But, they need to be hard-wired. Wagan Tech introduced their new DC to DC Battery Chargers in 2022, both a 25-amp model for $300, the $400 40-amp model that I installed.
New Hole Required
If the auxiliary battery to be charged is on the same chassis, like inside the same engine bay, the installation is easier. If secondary batteries are in a separate RV, the wiring needs to go from the host chassis into the recipient. If the RV is a trailer that is attached and disconnected regularly, then something like an Anderson plug provides a robust connector (and something I intend to add in the future).
With my Hallmark flatbed outfit, I directly connected new wires from the Cummins engine to the camper batteries, which required a new hole in my Hallmark. The process was not trouble free.
Parts and Supplies Matter
In an effort to avoid drilling a new hole, I attempted to use smaller but adequate 8-gauge gauge wires, running them alongside the existing Hallmark 7-way RV pigtail. The new positive and negative wires added too much girth to get the nut onto the knockout plate. This defeat came after hours spent running the wires from the engine bay, along the chassis, and then stuffing them next to the factory Hallamrk wiring pigtail and into the coach.
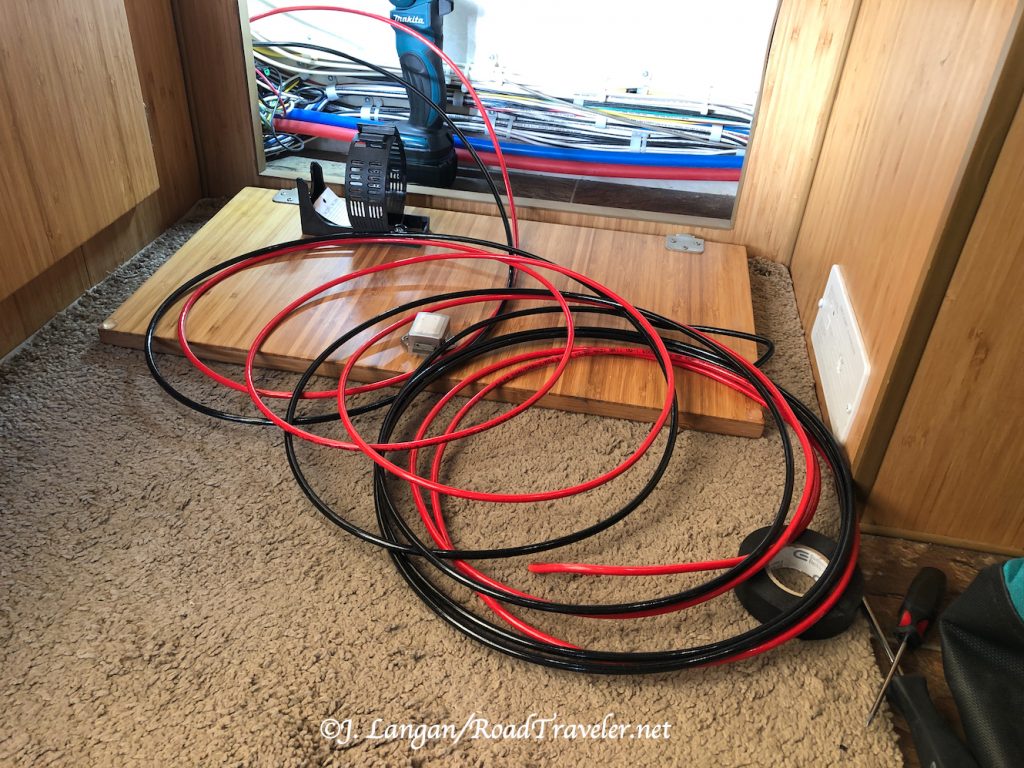
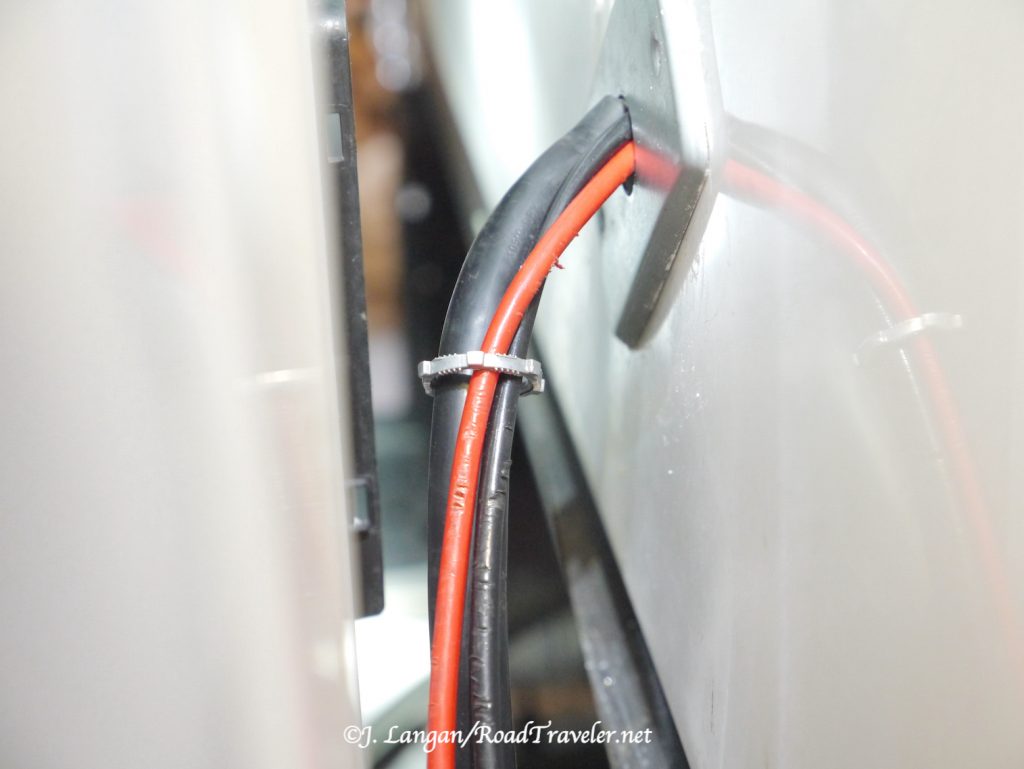


When it was obvious that drilling a new hole was required I decided to use larger 6-gauge wire, good for up to 32-feet. The finished total length was less than 20-feet so the wire will easily handle the amperage. Due to time constraints the wire was purchased from a nearby Home Depot, the trade-off being that it is not as flexible or easy to work with as ever thinker, larger welding cable.
Measure Multiple Times And Drill Once — A Nice Idea
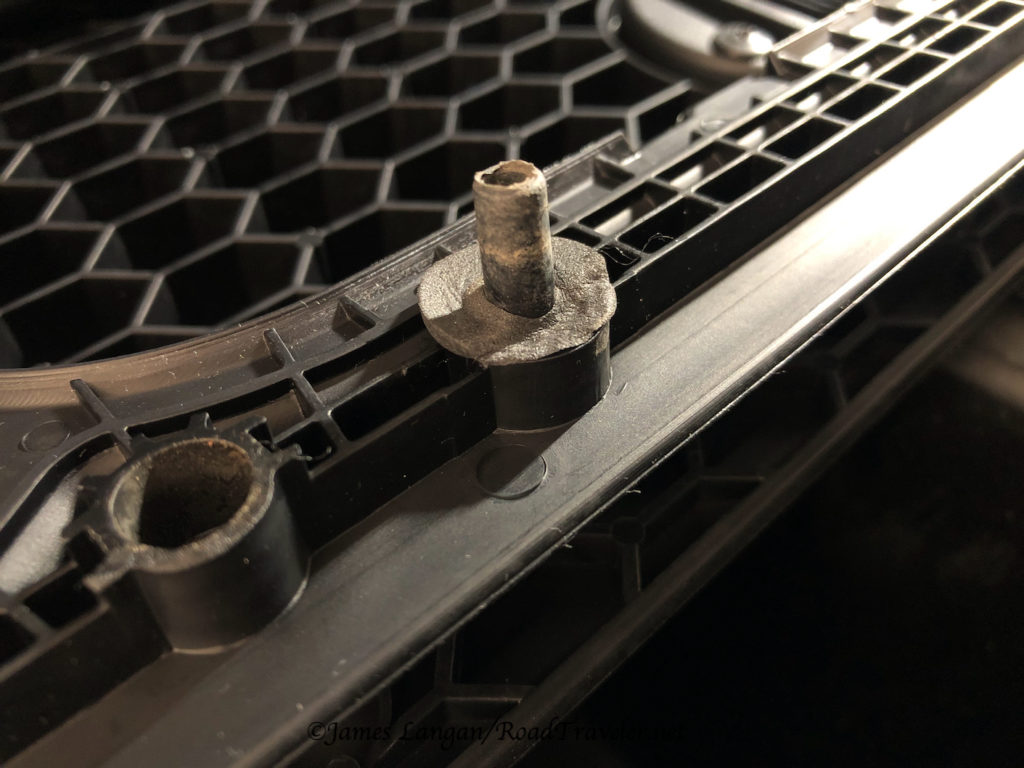
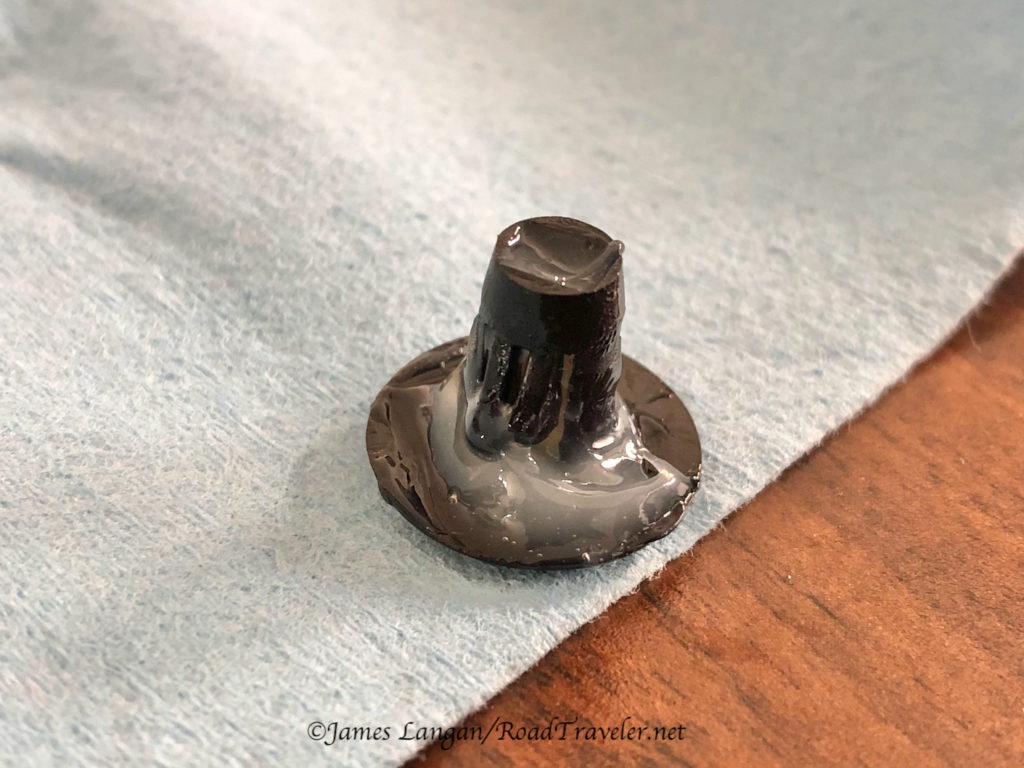
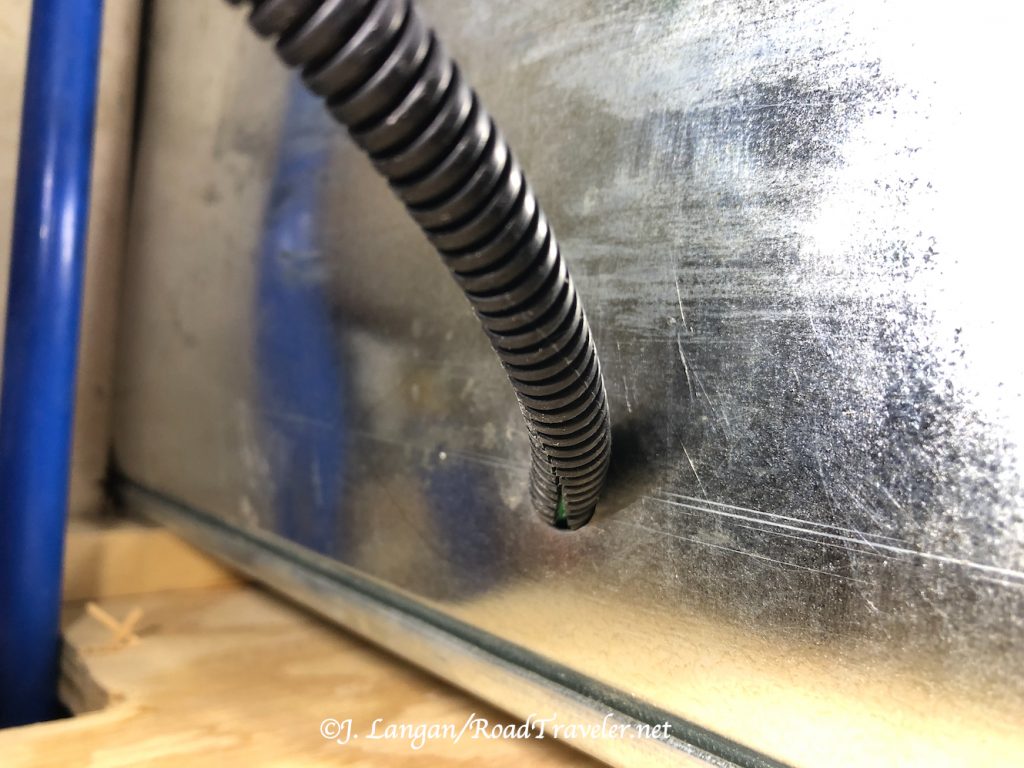
The new hole in the driver’s side front wall needed to go below the water heater and above the propane locker, and it needed to be approximately 1-inch diameter. After measuring and making countless trips from the front wall into the camper, I was confident about the placement before drilling the pilot hole. Using my cordless right angle drill, I nailed it, but I assumed the 7/8″ hole saw I had was big enough, and I made a nice, clean hole. However, it was too small for the knockout plate bolt to slide from inside the camper, clamped on the 6-gauge wires, through the wall to the exterior to reach the knockout plate nut.

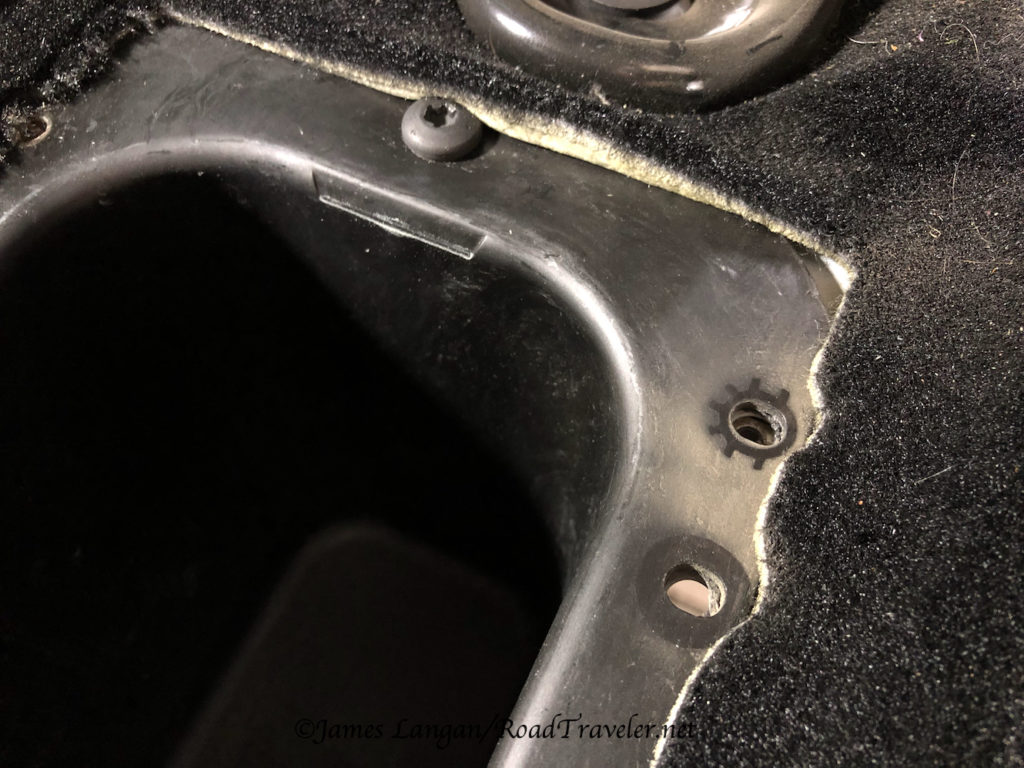
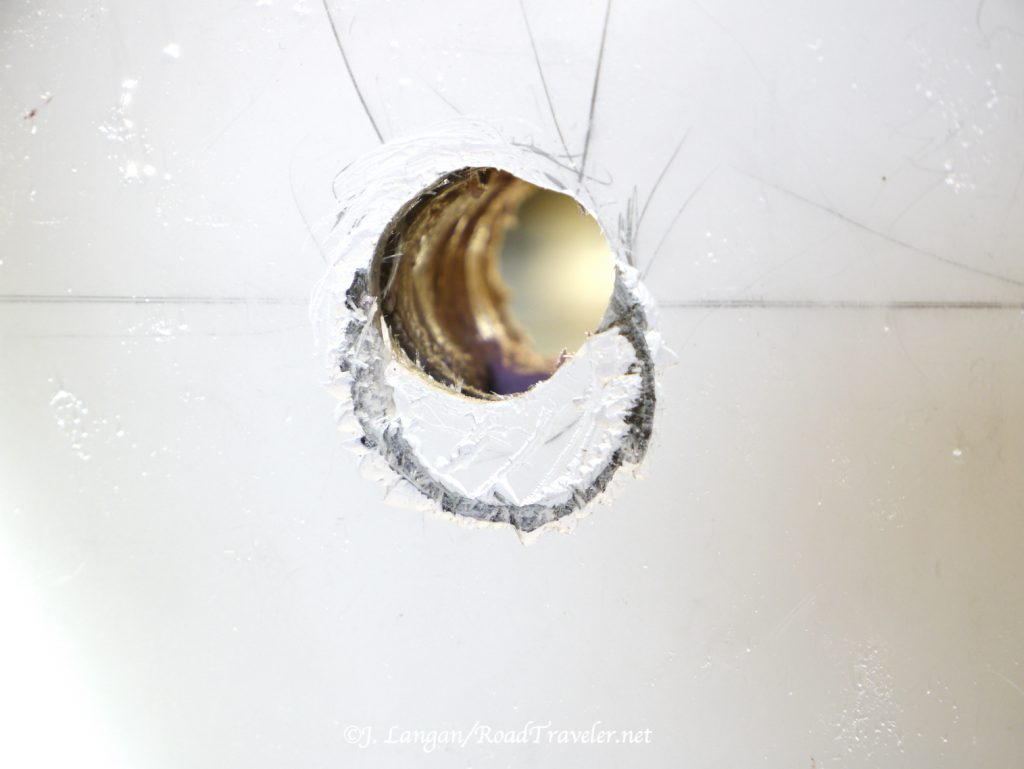
Back to Home Depot to buy a larger hole saw, something near 1 1/4″. As many do-it-yourself folks know, it is relatively easy to new to drill a clean new hole, but difficult (almost impossible) to cleanly make a hole slightly larger. A few times I slowly and carefully tried to get the larger hole saw started, but, of course, the saw just slid on the fiberglass. When trying gently does not work, what is the typical response? Add force.
The Neanderthal in me came out, and I leaned on the drill to make the saw bite into the fiberglass where I wanted; this was a bad idea. The saw walked on the slippery fiberglass surface, but with increasing force it eventually dug into the exoskeleton wall, making the scar you see in the photo below. I didn’t swear much, but I was slightly displeased with myself!

Disgusted, angry, and frustrated, there was no going back, and I still needed to enlarge the hole. My solution was what I should have done after discovering the hole was just a bit too small; I ran a half-inch bit around the circumference of the hole until it was big enough.
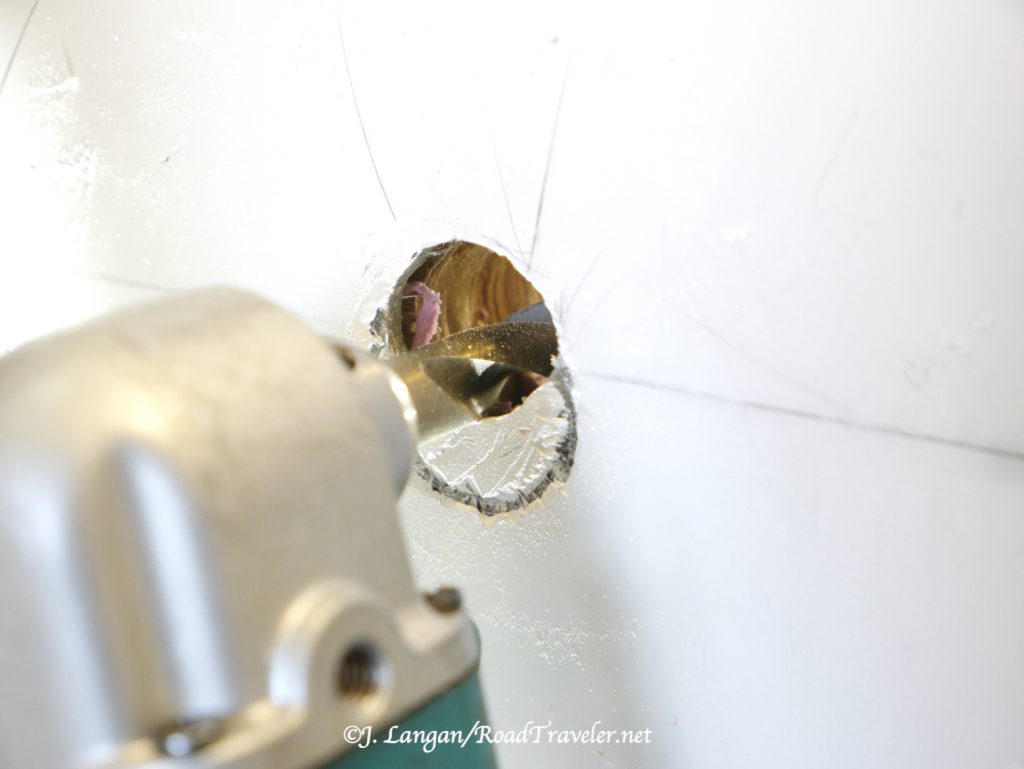

Thirty years ago this would have bothered me for weeks. I like to do clean, high-quality work. It’s covered by a plate and will never be an issue to anyone but me, and I’ve put it behind me. With the challenging part completed, it was time to finish the installation and get the Wagan Tech DC to DC Charger working.
Pulling And Connecting
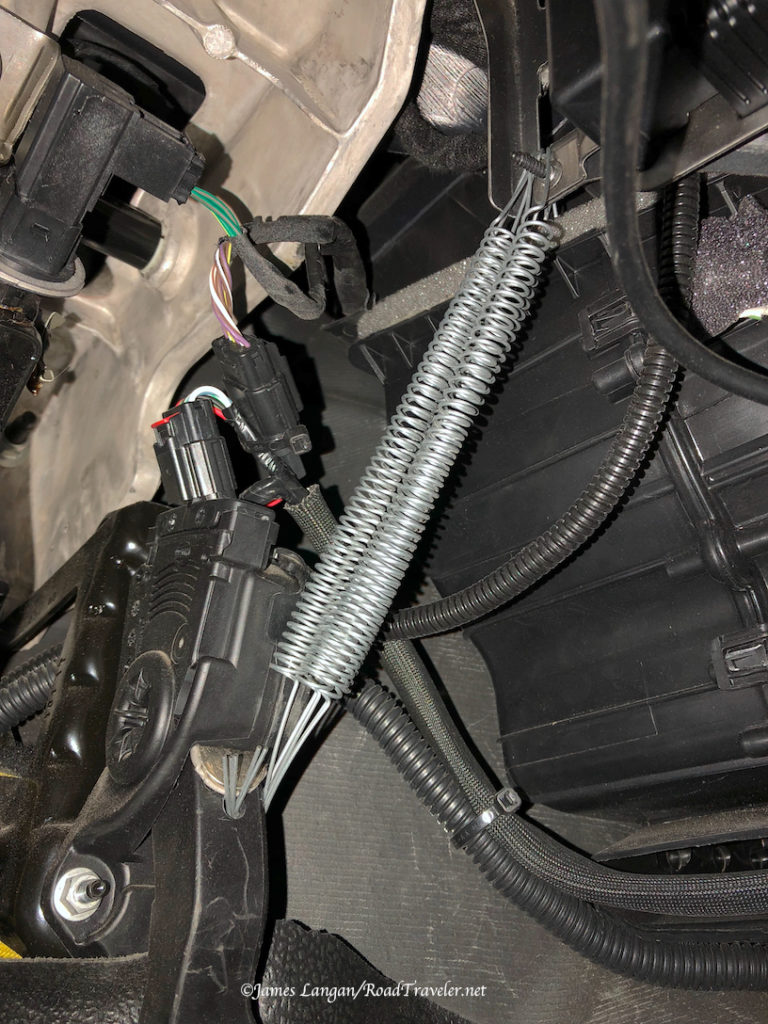
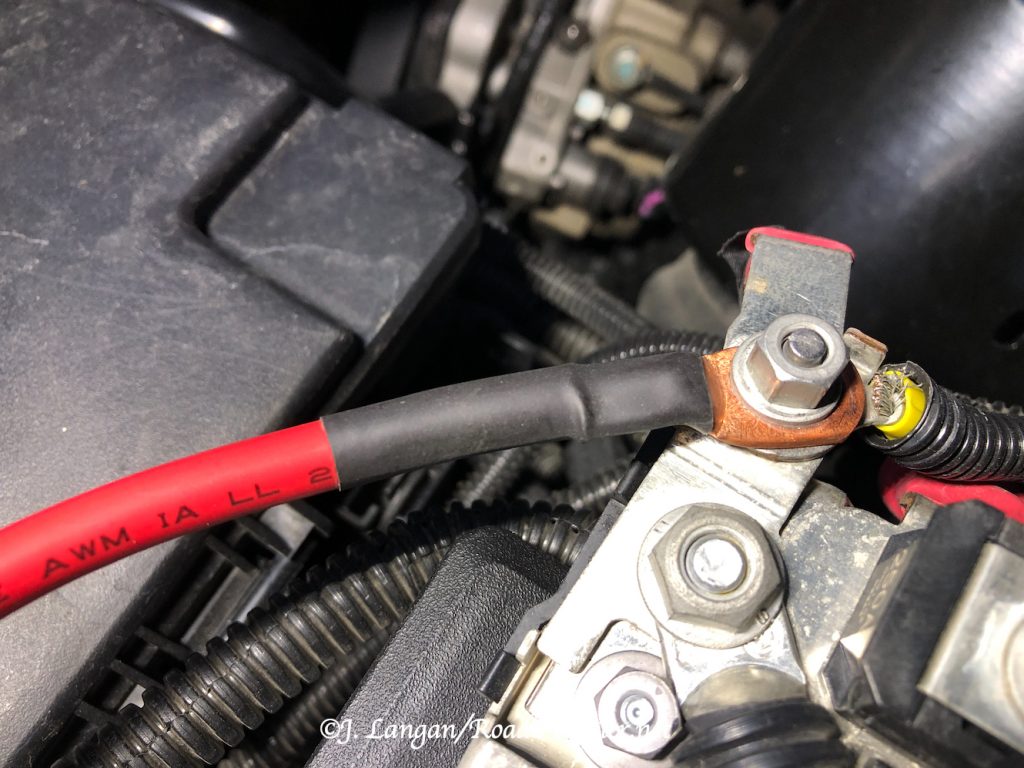
The rest of the installation was straightforward and easy, and there were no more hiccups. I fed the 6-gauge wire through two rubber firewall boots to provide a weather barrier, one from the camper front and one from the inside, then along the frame and into the engine compartment to the driver’s side battery.
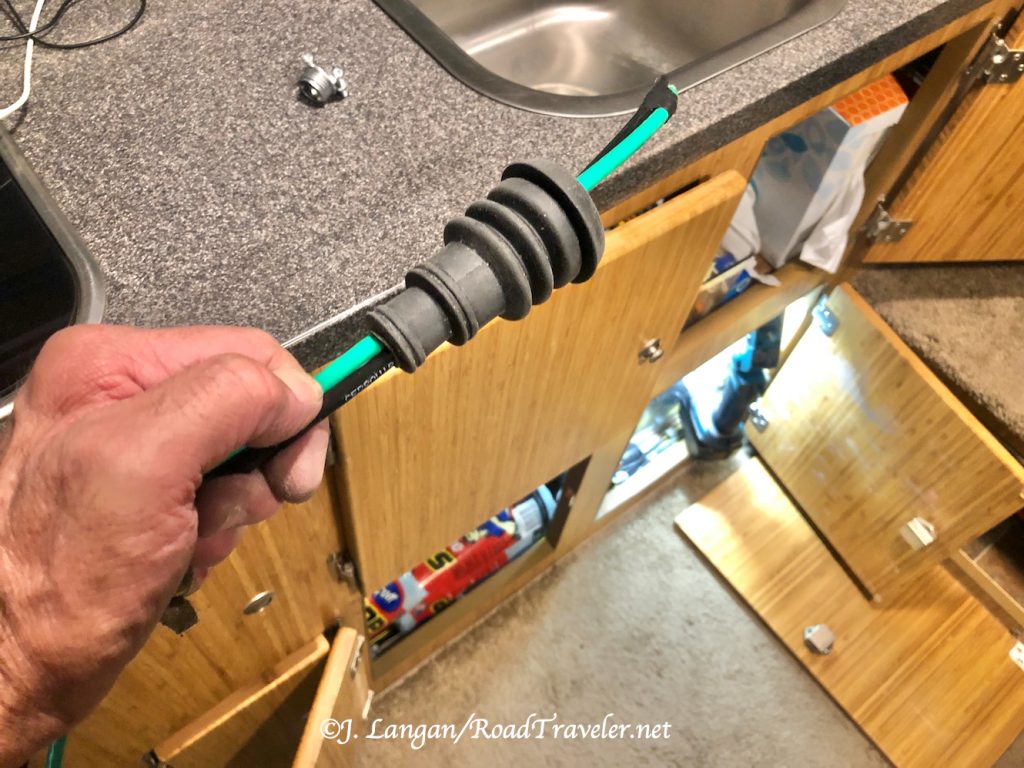
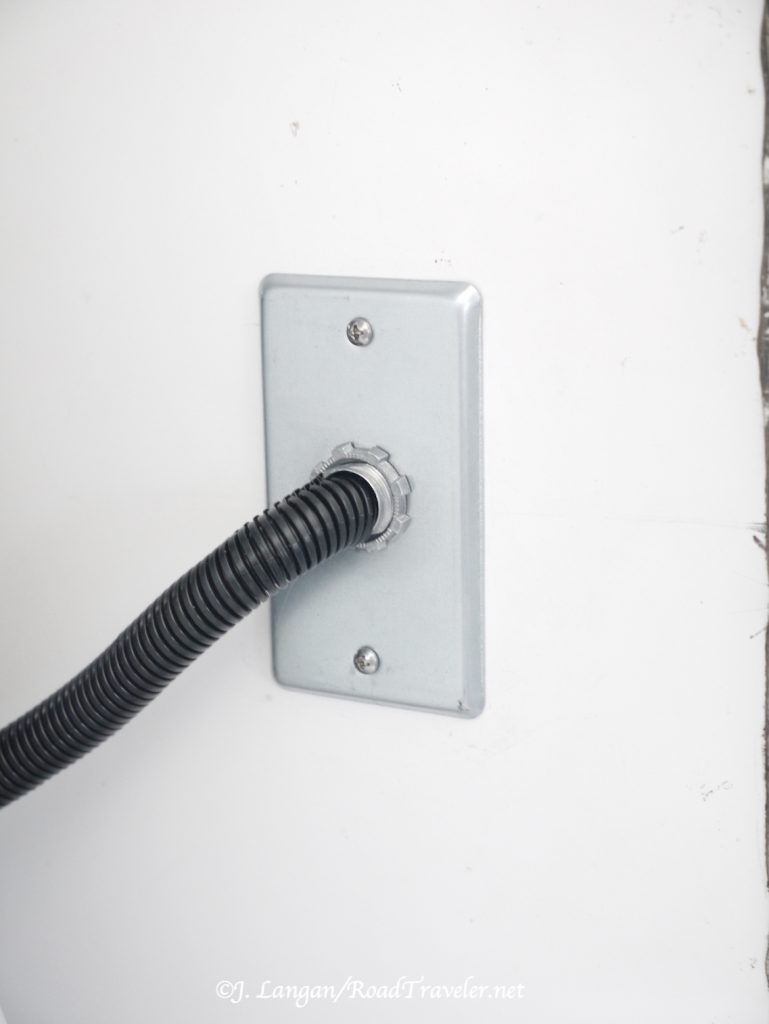


This Wagan 40-amp unit requires two 60-amp fuses, one as close to the engine bay battery as practical, and another on the Wagan charger output line near the auxiliary batteries. Bolt-down fuses are recommended because they have lower resistance than blade type, which can have higher resistance and create excessive heat. However, the blade-type Maxi fuses are what I found locally, and I’m confident they’ll be sufficient.

With the incoming hot and ground wires from the engine connected to the Wagan charger, another small hole was drilled in the Hallmark’s battery box to run a hot lead from the charger to my two 100-amp lithium RV batteries.

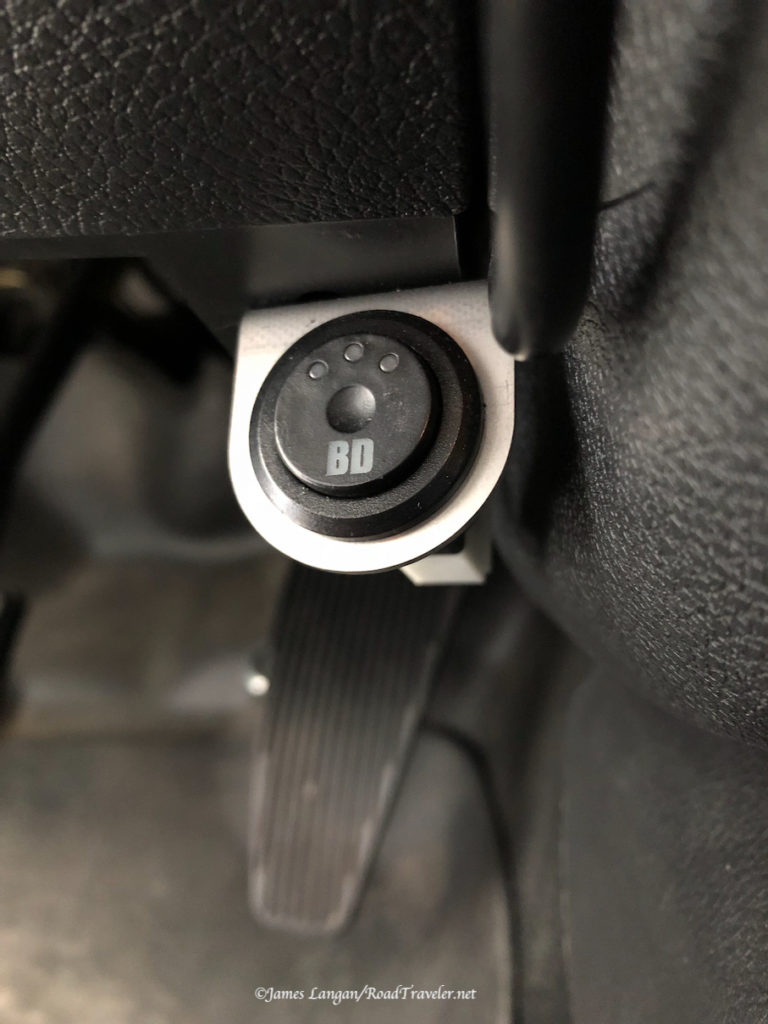
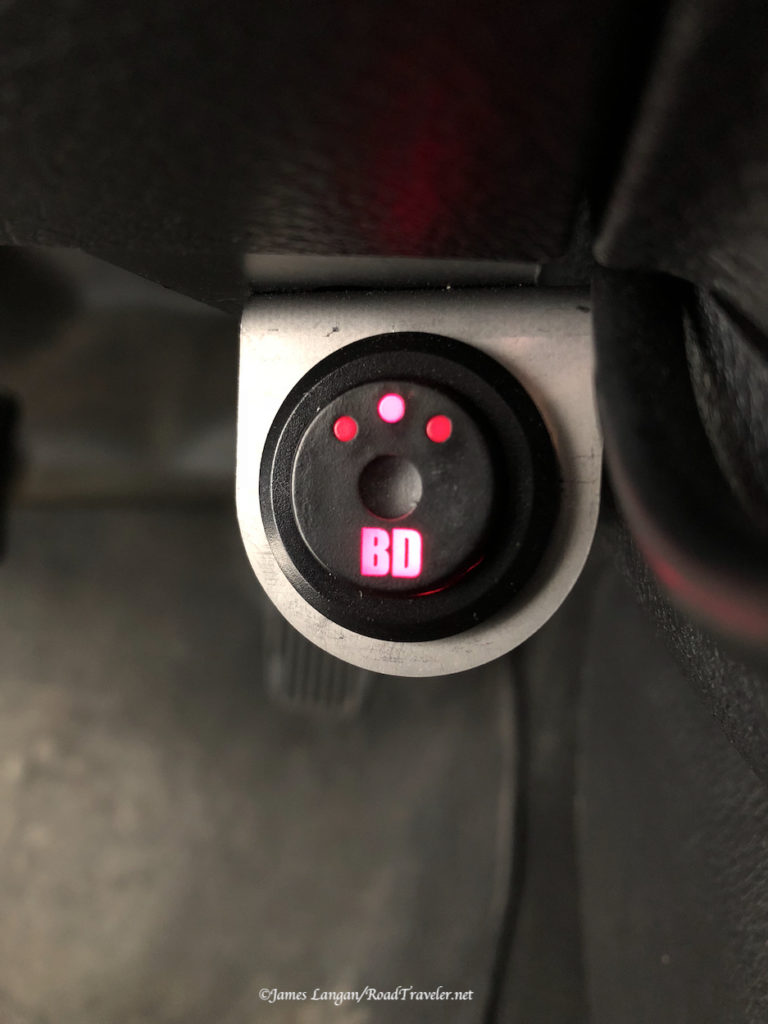
With the fuses inserted I had the appropriate blinking lights on the front of the Wagan DC to DC Battery Charger; one light showing it was connected to the alternator, and after changing the battery type to LifePO4, that light was on as well. The unit is capable of working with standard, gel, AGM, and lithium batteries.
Wagan Tech’s instructions are short, simple, and easy to follow, and folks capable of doing basic wiring will likely have no problems doing this themselves. Because of the largish 6-gauge wire and connectors I used a hydraulic crimping tool, and I covered the ends with heat shrink, routed the wires as cleanly as possible, and protected them with split-loom.

Mounting Options
The Wagan charger is designed for a variety of installation environments, including chassis rail, engine bay, interior cabin, etc. The unit has been designed to work in vibrating, wet, dusty and muddy environments, and can withstand temperatures of up to 176°F, so it can be installed in the engine bay. However, to get better charging efficiency, mounting the charger away from high-temperature parts is preferred.
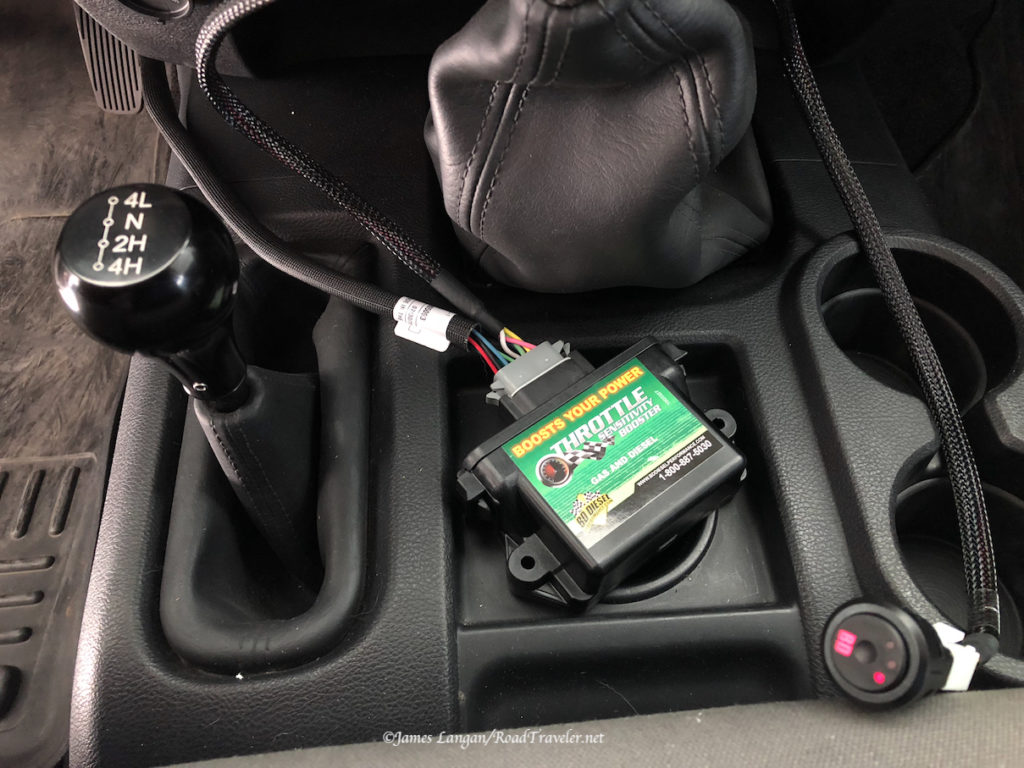
I simply stuck it to the bottom galley shelf with mounting tape, between the propane locker and battery box. I may add screws later if this is the charger’s permanent home, but it’s not going anywhere on this flat surface.

Wagan Tech DC Charger Works
Using more amperage than is being generated during long road trips should be a thing of the past. We’re unlikely to need a generator unless we want to run our air conditioner, in which case we would tote our larger Honda 2000.
Pumping a massive 40 amps per hour into the Hallmark’s lithium batteries means it takes little driving to fill them; every time we make camp the batteries will probably be full. Even if the lithiums were completely drained we could replenish all 200 amps in five hours!
Our initial adventures with Wagan DC to DC 40-amp Charger installed were extremely encouraging, the camper batteries were full whenever we stopped, and the voltage was high, as if we’d been connected to shore-power.
The Cummins is a large and expensive generator, but because we are already traveling, delivering essentially free electricity from our alternator to the camper batteries is a game-changer. Why did we wait so long to add something like Wagan’s 40A DC to DC Battery Charger?
Drive diesel and tell ‘em you saw it in the TDR! (A version of this article was previously published in the Turbo Diesel Register magazine.)
Tell ’em you saw it on RoadTraveler.net
Copyright J. Langan/RoadTraveler. All Rights Reserved
Instagram: @RoadTraveler
Twitter: @RoadTravelerNet
YouTube: RoadTravelerNet
Resource:
Wagan Tech: wagan.com